

The moment of inertia plays the role in rotational kinetics that mass (inertia) plays in linear kinetics-both characterize the resistance of a body to changes in its motion. Definition & Formula Moment of Inertia is a physical quantity that resist to transitional motion. MR2 is the moment of inertia of the pulley. Since inertia depends upon the axis around which the component rotates, we can start by considering the applied load and the belt together, since they both rotate around the axis of the driven pulley. s Moment of Inertia Calculator is an online physics tool to measure the rotational inertia of different objects of most common shapes based on the mass distribution and their axis, in both US customary & metric (SI) units. m 2) in SI units and pound-foot-second squared (lbf Answer: To find Ix, the moment of inertia about the symmetry axis parallel to the x-axis, we.Moments of inertia may be expressed in units of kilogram metre squared (kg The amount of torque needed to cause any given angular acceleration (the rate of change in angular velocity) is proportional to the moment of inertia of the body.
#CALCULATE MOMENT OF INERTIA PULLEY WITH MULTIPLE SHAPES FREE#
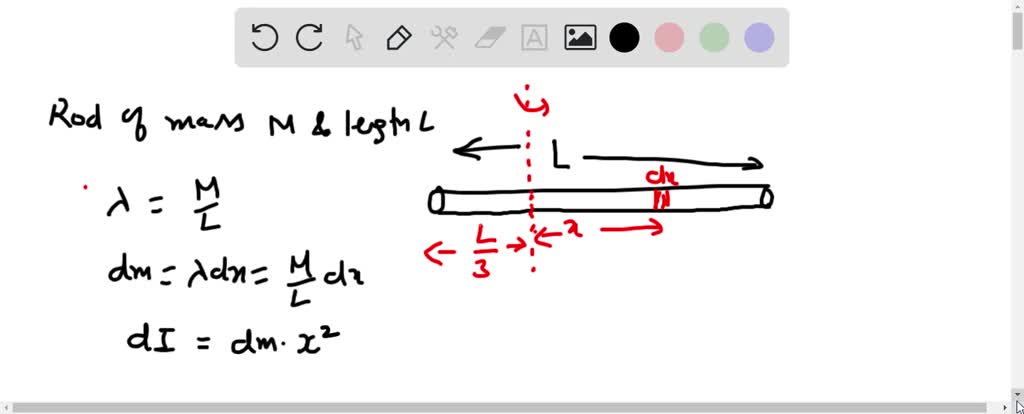
When a body is free to rotate around an axis, torque must be applied to change its angular momentum. For bodies free to rotate in three dimensions, their moments can be described by a symmetric 3-by-3 matrix, with a set of mutually perpendicular principal axes for which this matrix is diagonal and torques around the axes act independently of each other. Its simplest definition is the second moment of mass with respect to distance from an axis.įor bodies constrained to rotate in a plane, only their moment of inertia about an axis perpendicular to the plane, a scalar value, matters. The moment of inertia of a rigid composite system is the sum of the moments of inertia of its component subsystems (all taken about the same axis). If not given, create your axes by drawing the x-axis and y-axis on the boundaries of the figure. This formula applies to every bit of the object that’s rotating each bit of mass has this kinetic energy. Identify the x-axis and y-axis of the complex figure. It is an extensive (additive) property: for a point mass the moment of inertia is simply the mass times the square of the perpendicular distance to the axis of rotation. where m is the mass of the object and v is the speed. The differential element dA has width dx and height dy, so dA dx dy dy dx. It depends on the body's mass distribution and the axis chosen, with larger moments requiring more torque to change the body's rate of rotation. To find the moment of inertia, divide the area into square differential elements dA at (x, y) where x and y can range over the entire rectangle and then evaluate the integral using double integration. The moment of inertia, otherwise known as the mass moment of inertia, angular mass, second moment of mass, or most accurately, rotational inertia, of a rigid body is a quantity that determines the torque needed for a desired angular acceleration about a rotational axis, akin to how mass determines the force needed for a desired acceleration.

To improve their maneuverability, war planes are designed to have smaller moments of inertia compared to commercial planes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
